Himani B Pandya
S.B.K.S Medical College, India
Title: Prevalence and microbiological diagnosis of H. pylori infection and its antibiotic resistance pattern in patients with acidpeptic disorders
Biography
Biography: Himani B Pandya
Abstract
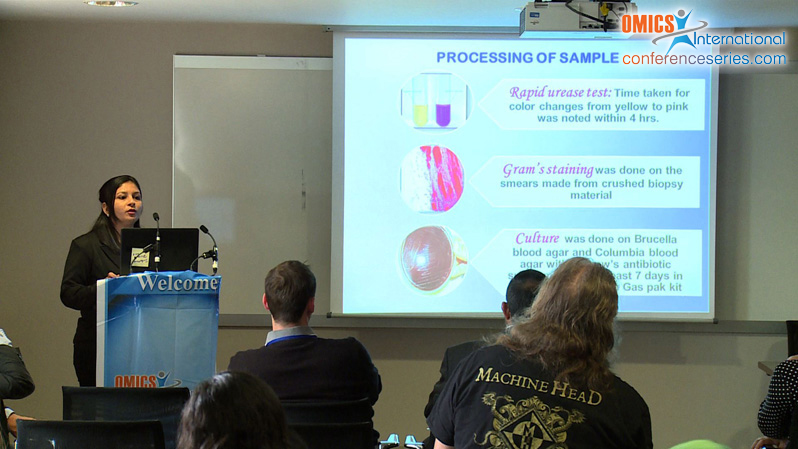
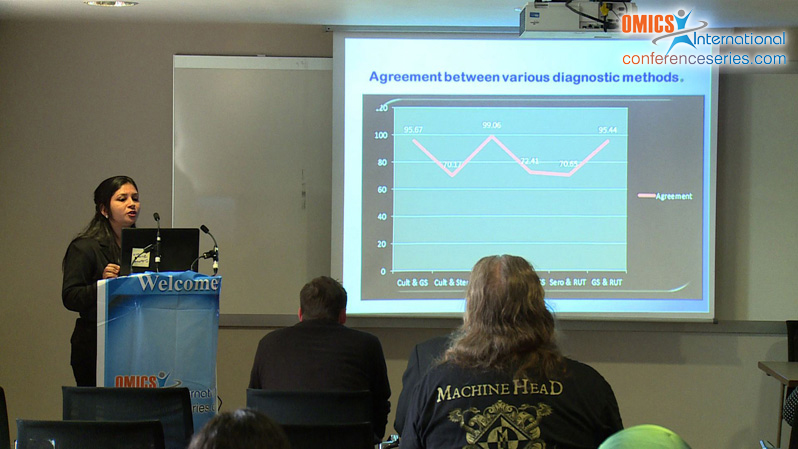
Helicobacter pylori play major roles in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer diseases, chronic antral gastritis, Gastric ulcer diseases and, possibly Gastric cancer. Intend of the study was to find out the prevalence of H. pylori infection with reliable diagnostic method along with its antibiotic resistance pattern. From 855 symptomatic patients, four antral biopsies were collected in a sterile BHI broth and were processed for Rapid urease test, Gram’s staining, Culture and histopathological staining (Warthin-Starry stain and Giemsa) and serum sample were tested for H. pylori IgG and IgA antibody by using ELISA. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of 80 clinical isolates was performed by Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. Prevalence rate of H. pylori infection was found 14.6% (125/855), infection was found highest in gastritis patients. Sensitivity of serology (98.8%) and Gram’s staining (96.8%) was highest, while Rapid Urease test, Culture and Gram’s staining showed highest specificity of 99.9%, 100% and 98.5% respectively. Sensitivity of IgG-ELISA was better than IgA-ELISA. Primary antimicrobial resistance of H. pylori to metronidazole was very high (83.8%), followed by amoxicillin (72.5%), clarithromycin (58.8%) and tetracycline (53.8%). The association of Gram stainingand rapid urease testis best for quick evaluation of the infectious status of patient. Our results also recommend the need of sensitivity profile regionally and periodically before the general use of an eradication schedule.
Speaker Presentations
Speaker PPTs Click Here